The Perils of Prescription Drug Addiction

Medically Verified: 2/1/24
Medical Reviewer
Chief Editor

All of the information on this page has been reviewed and verified by a certified addiction professional.
The Perils of Prescription Drug Addiction
Prescription drugs are used to treat discomfort, illnesses, and diseases. For many people, these medications improve their quality of life. Sometimes, these medications make the difference between life and death. Although these medications are legal when prescribed by a doctor, many of them can be abused and lead to addiction.
Some people who abuse prescriptions take their medication more frequently or in higher doses than prescribed. Others take prescription drugs recreationally and purchase them on the street. People may think prescription drugs are safe because they are used by doctors. However, many prescription drugs are dangerous when abused. The most popular medications of abuse include benzodiazepines, opioids, and stimulants. When addiction develops, overcoming prescription drug addiction without professional help can be extremely challenging.
Prescription Drug Abuse
The National Institute on Drug Abuse defines prescription misuse as “taking a medication in a manner or dose other than prescribed; taking someone else’s prescription, even if for a legitimate medical complaint such as pain; or taking a medication to feel euphoria.” [1] Approximately 48 million people, or 20% of the U.S. population, have used prescription drugs for non medical reasons.[2] Similarly, in the last 15 years, overdose deaths involving prescriptions have increased by nearly 20%.
People abuse prescription medications for a variety of reasons. Sometimes, prescriptions are abused to cope with mental health symptoms. On the other hand, some people abuse certain prescriptions to either relax or boost their focus and energy levels. However, many people abuse prescriptions to feel the euphoric effects that they produce.
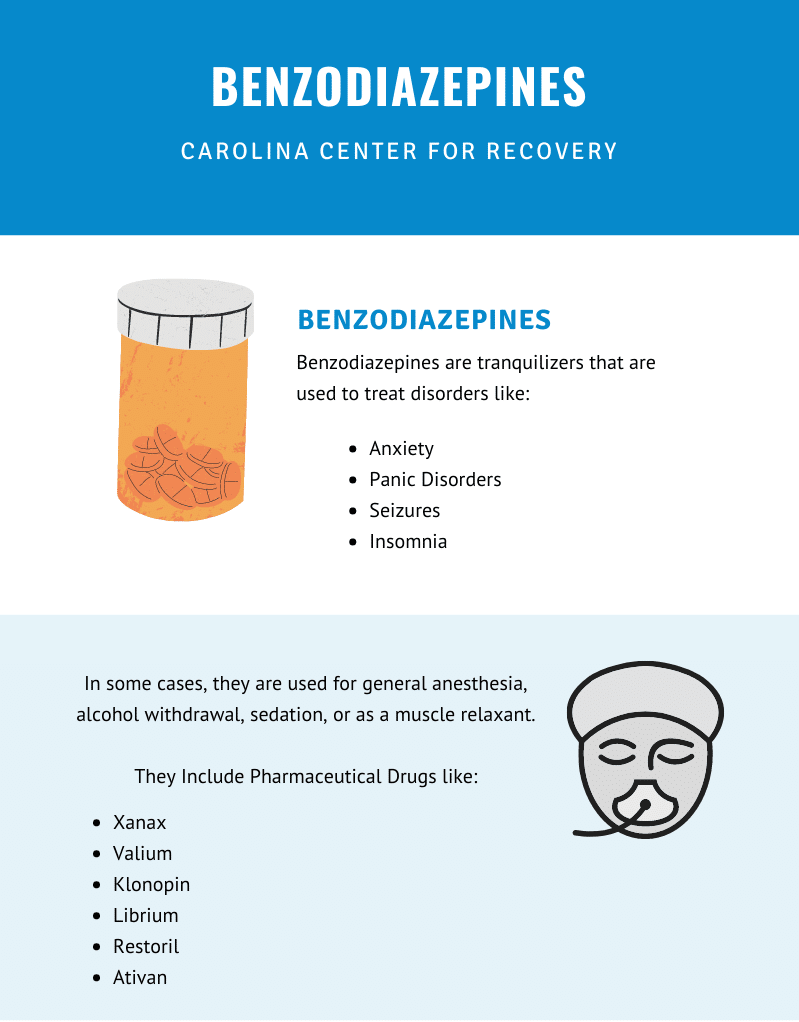
Benzodiazepine Abuse
Benzodiazepines are medications like Xanax (alprazolam), Valium (diazepam), and Klonopin (clonazepam). Medications in this class are used to treat a wide array of legitimate medical conditions, such as:
- Anxiety
- Alcohol withdrawal
- Sleep disorders
- Seizures
- Muscle disorders
- Pre-surgery medication
Stimulant Abuse
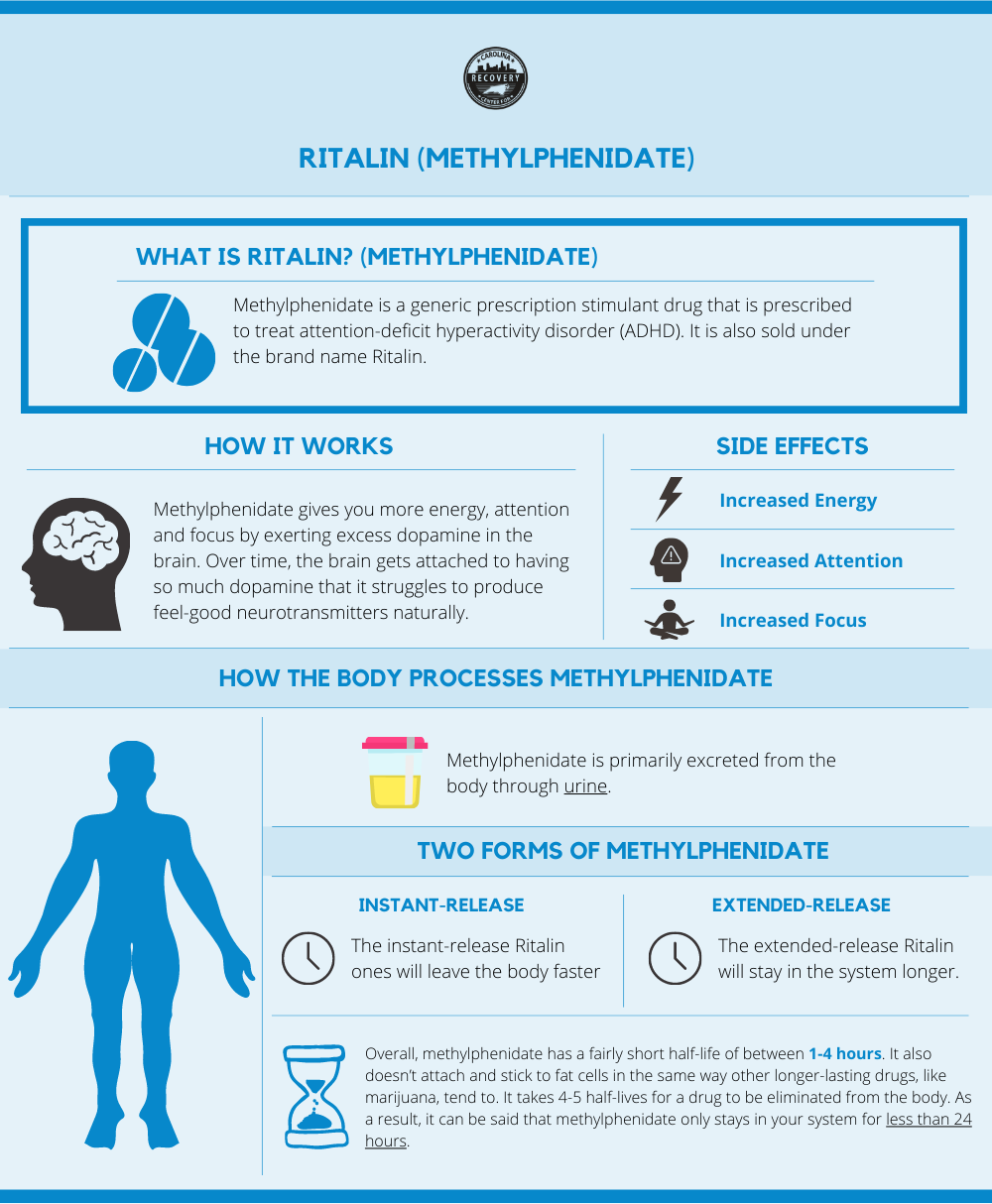
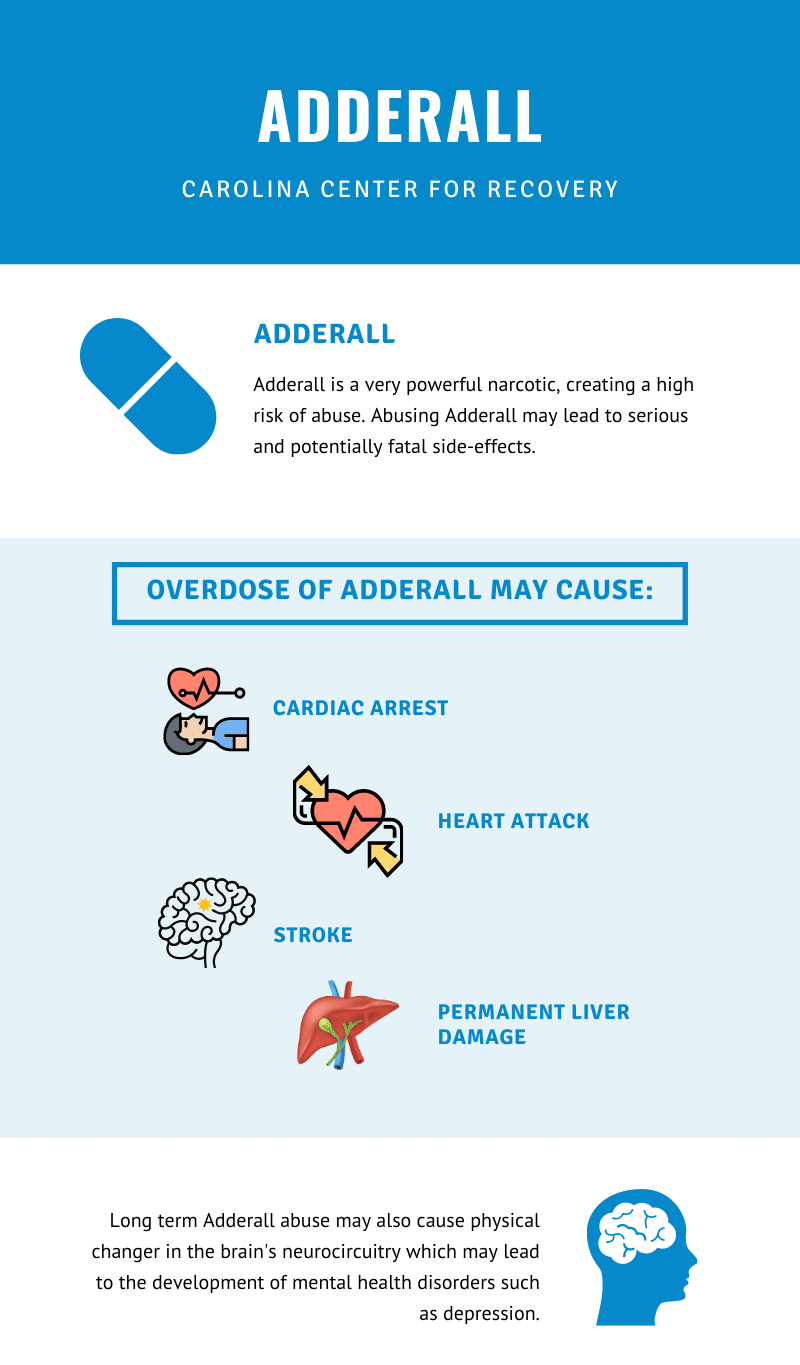
Prescription stimulants are used to treat attention–deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). In addition, these medications are sometimes used to treat narcolepsy or aid in weight loss. Stimulants include Ritalin (methylphenidate), Adderall (amphetamine), Dexedrine (dextroamphetamine) and more.
When stimulants are abused, a person can experience any or all of the following symptoms:
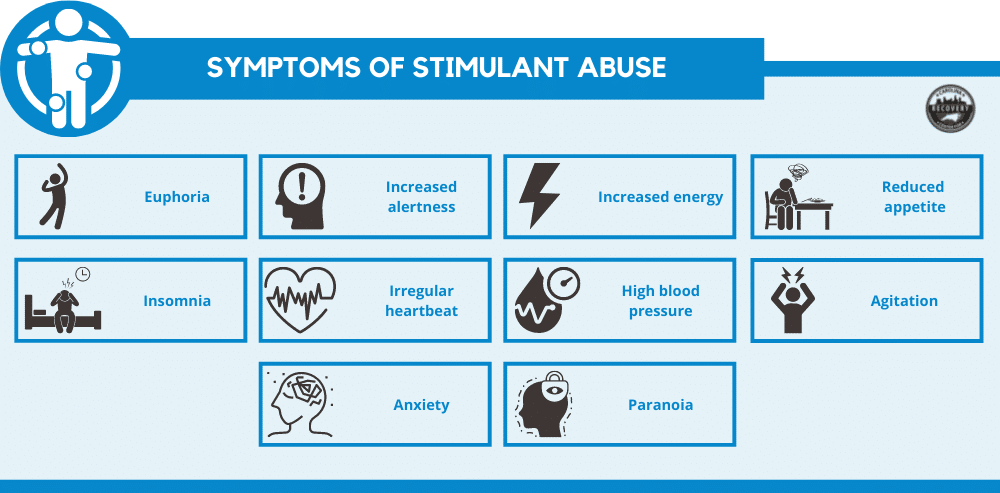
- Euphoria
- Increased alertness
- Increased energy
- Reduced appetite
- Insomnia
- Irregular heartbeat
- High blood pressure
- Agitation
- Anxiety
- Paranoia
Prescription stimulants increase the levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain. Dopamine controls the reward system. Consequently, when a stimulant is abused and the brain is accustomed to high levels of dopamine, the mind and body will begin to crave more and more of the drug. While overdoses on stimulants aren’t as common as opioid or benzo overdoses, when taken in high doses an overdose or cardiac arrest may occur. Long term stimulant abuse can result in extreme anxiety, heart problems, and intense paranoia.[4]
Prescription Opioid Abuse
Prescription opioids, such as Oxycontin, Percocet, and hydrocodone, are frequently used to treat moderate to severe pain. Opioids, taken in high doses, create a strong sense of euphoria, relaxation, and sedation. They are also physically addictive as well. After all, a person can get physically addicted to prescription opioids after only 7 days. When a person is abusing prescription opioids, they may experience the following symptoms:
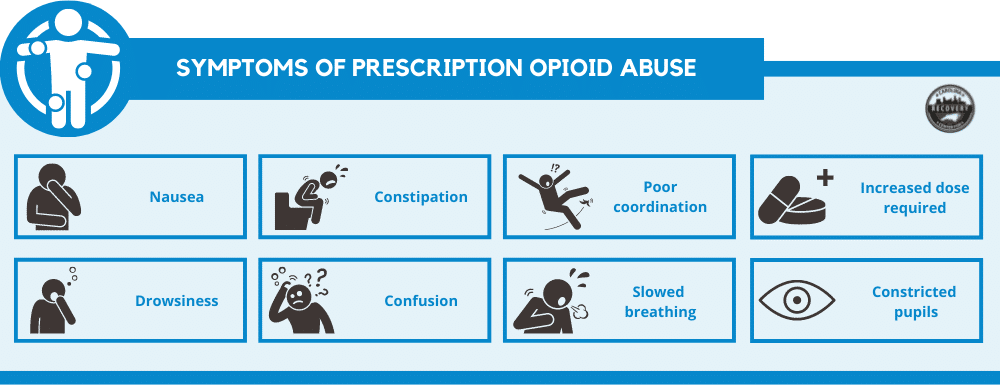
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Poor coordination
- Increased dose required
- Drowsiness
- Confusion
- Slowed breathing
- constricted pupils
The CDC reports that approximately 46 people die each day from a prescription opioid overdose. Opioid addiction can involve excruciating withdrawals that often make recovery impossible without professional help.[5]
Signs of Prescription Drug Addiction
When a person is abusing prescription drugs, there are several signs and symptoms that he or she may display. While some signs will vary from drug to drug, some signs that indicate prescription drug addiction include:
- Going to multiple doctors to get a prescription
- Running out of prescriptions early
- Stealing, forging, or selling prescriptions
- Extreme mood swings
- Increase or decrease in energy
- Poor decision-making skills
- Lying to family members and loved ones
- Increased problems at work, home, or school
- Continued use despite negative consequences
For people suffering from prescription drug addiction, a trusted addiction treatment center can help.
Treatment for Prescription Drug Addiction
The first step towards recovery from prescription drug addiction begins with asking for help. Typically, a person will require a medical detox to ensure that they detox safely. Once a person is medically stable, they can begin a comprehensive treatment program.
Treating prescription drug addiction usually requires more than abstinence. After all, addiction can affect a person’s mental, physical, and emotional states. As a result, a treatment program that offers individualized programs is crucial. Behavioral therapy, group, and individual treatment can provide individuals with the tools needed to recover.
If you or a loved one is suffering from prescription drug addiction and are ready to leave the habit behind, contact an addiction specialist in North Carolina today.
References:

